The Ultimate Guide to Psychiatry CPT Codes
CPT coding for psychiatry can feel overwhelming — especially with overlapping evaluation and management (E/M) and therapy codes. Getting them wrong can lead to claim denials or underpayments.
This guide breaks down the most important psychiatry CPT codes you need to know, along with examples, documentation tips, and billing best practices for 2025.
Understanding Psychiatry CPT Codes
Psychiatry billing includes two main code categories:
- Evaluation and Management (E/M) Codes — for psychiatric diagnostic evaluations and medication management.
- Psychotherapy Codes — for individual, group, or family therapy sessions.
Often, both are billed together when therapy and evaluation occur during the same session.
Common CPT Codes for Psychiatrists
1. 90791 – Psychiatric Diagnostic Evaluation
Used for initial assessments (no medical services).
Typical Use: First visit with a new patient for diagnosis and evaluation.
2. 90792 – Psychiatric Diagnostic Evaluation with Medical Services
Used when the psychiatrist performs a full evaluation plus medical management.
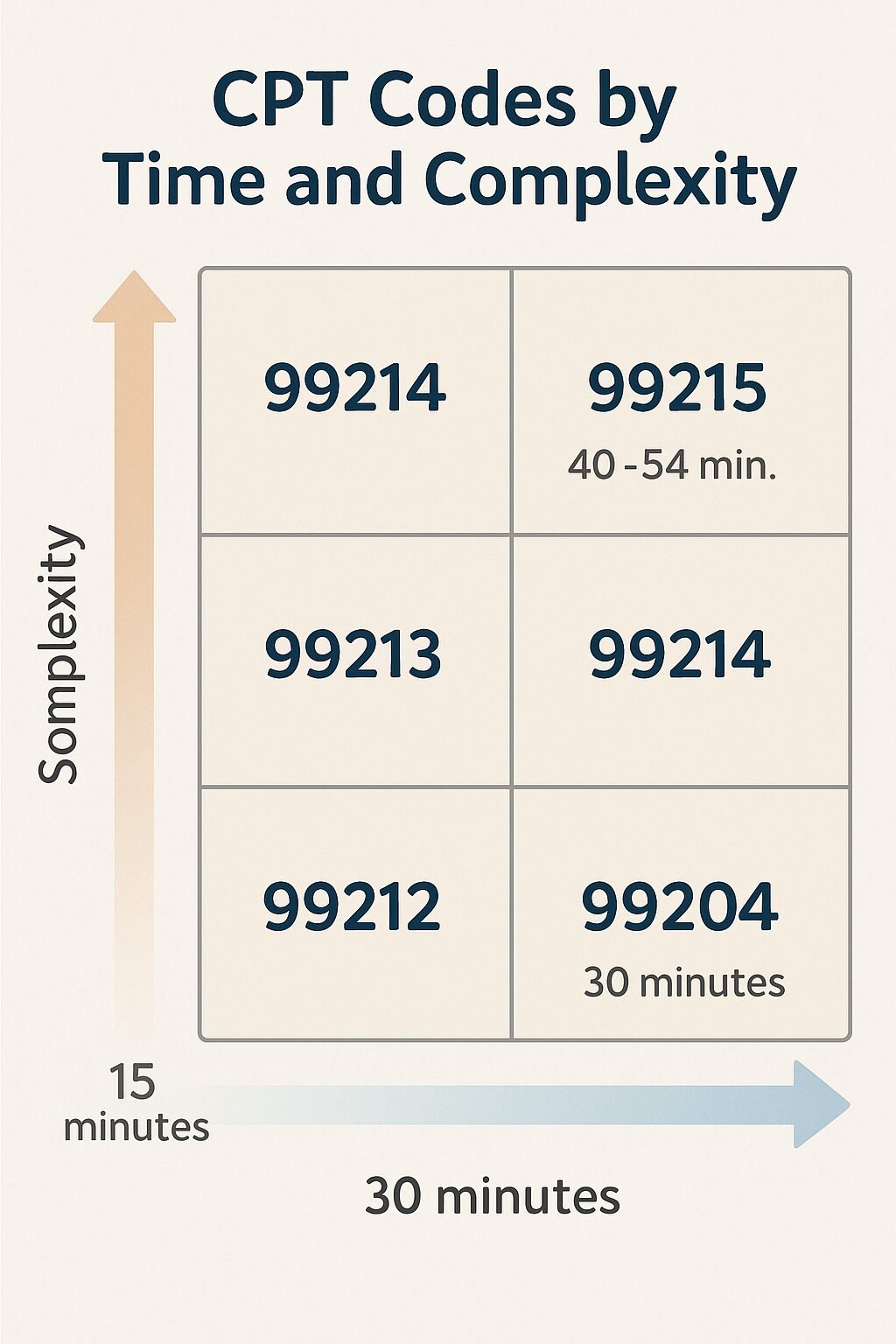
3. 99213 / 99214 / 99215 – E/M Codes
Used for ongoing medication management and follow-ups.
- 99213: Low complexity (10–15 min)
- 99214: Moderate complexity (20–30 min)
- 99215: High complexity (40+ min)
4. 90832 / 90834 / 90837 – Psychotherapy Codes
- 90832: 30 minutes
- 90834: 45 minutes
- 90837: 60 minutes
5. 90833 – Psychotherapy Add-On (with E/M Service)
Used when therapy is provided alongside medication management (e.g., 99214 + 90833).
6. 90846 / 90847 – Family or Couples Therapy
- 90846: Without patient present
- 90847: With patient present
7. 90785 – Interactive Complexity Add-On
Used when communication challenges exist (e.g., children, trauma cases, third-party involvement).
Documentation Tips for Psychiatry Billing
- Clearly separate E/M and therapy time in notes.
- Include total time, content discussed, and medical decision-making.
- For 90833, document distinct therapy elements beyond medication management.
- Always justify the use of 90785 with examples (e.g., interpreter, emotional dysregulation).
Common Psychiatry Billing Mistakes to Avoid
❌ Using 90837 without adequate session time (less than 53 minutes).
❌ Billing 90833 without supporting psychotherapy documentation.
❌ Mixing E/M and therapy codes incorrectly.
❌ Forgetting to apply modifier 25 when required.
Psychiatry CPT Code Billing Example
Scenario:
A psychiatrist provides a 25-minute medication review and 20 minutes of psychotherapy.
Correct Coding:
- 99214 (E/M moderate complexity)
- +90833 (psychotherapy add-on)
- Modifier 25 if required by payer
Staying Updated with CPT Code Changes
CPT codes evolve every year. Always check:
- AMA CPT Code updates (January each year)
- Payer bulletins for policy changes
- Medicare Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs)
Simplify Psychiatry Billing with QuantiSurge
At QuantiSurge Billing, we help psychiatrists and mental health providers submit clean, accurate claims using the right CPT combinations.
GET IN TOUCH
Schedule a Visit
Frequently Asked Questions
Praesent sapien massa, convallis a pellentesque?
Vestibulum ac diam sit amet quam vehicula elementum sed sit amet dui. Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Donec velit neq.
When should I use 90833?
Use 90833 when psychotherapy is performed alongside E/M services like medication management.


Hey there, You have performed a great job. I’ll certainly digg it and in my opinion suggest to my friends. I’m sure they’ll be benefited from this web site.
Regards for all your efforts that you have put in this. very interesting information.
Your insights are a refreshing take in a world full of noise, and I’d love to see you unpack how these ideas intersect with emerging trends, like AI ethics or sustainable living. Your knack for simplifying the complex is remarkable. Thanks for always delivering such provocative content. excited for more!
Digital Space: https://talkchatgpt.com/
чат дпт на русском
When I originally commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get several emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Many thanks!
Whats up very cool website!! Guy .. Beautiful .. Superb .. I’ll bookmark your website and take the feeds also…I’m happy to search out a lot of helpful info here within the submit, we’d like develop more techniques on this regard, thanks for sharing.
I’ll right away seize your rss as I can not to find your email subscription hyperlink or newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please allow me realize in order that I could subscribe. Thanks.
I do agree with all the ideas you’ve presented in your post. They’re really convincing and will definitely work. Still, the posts are too short for newbies. Could you please extend them a little from next time? Thanks for the post.
Wow! This could be one particular of the most beneficial blogs We’ve ever arrive across on this subject. Actually Excellent. I am also an expert in this topic so I can understand your effort.
Hello there, simply was alert to your weblog thru Google, and located that it’s truly informative. I am going to watch out for brussels. I’ll be grateful if you proceed this in future. Lots of folks will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Greetings from Ohio! I’m bored to tears at work so I decided to check out your site on my iphone during lunch break. I really like the information you provide here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m amazed at how quick your blog loaded on my phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyhow, great blog!
Keep working ,fantastic job!
Wow, incredible weblog structure! How lengthy have you ever been blogging for? you made blogging glance easy. The overall look of your website is great, as smartly as the content!